
环境污染生物控制技术研究室主要以环境生物技术为核心,开展污染物无害化处理和资源化利用方面的研究。研究室现有教师6人,共培养博士和硕士100余人。近5年来,承担国家高技术研究发展计划(863)课题、科技支撑计划、国家自然科学基金项目、国家重大专项等20余项,承担企业委托的污染治理项目50余项,发表SCI收录论文100余篇,授权专利20余件。
本研究室主要面向环境中难降解污染物、污水中氮磷营养物质,烟气中氮、硫的污染问题,开展污染物新型生物处理与资源化技术的研发,并形成一套针对复杂体系中微生物群落动态及功能基因解析的配套方法。近年来,研究室还自主研发出了高效烟气脱硫、脱硝及资源化技术,为我国开展节能减排工作提供理论和技术支持。
The main researches focus on pollutant degradation and resource utilization with biotechnology. There are currently 6 faculties in our group. More than 100 high-quality students have graduated with master’s or doctoral degree during the past decade. Since 2008, we have carried out tens of national projects, including key projects and general projects funded by National Natural Foundation of China, projects funded by National High-tech R&D Program (863 program), and National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. In addition, over 50 pollution treatment projects of different industries have been completed. More than 200 research papers have been published in international peer-reviewed journals and 20 China patents have been authorized during the past 5 years.
The laboratory targets on biological treatment of refractory pollutants, nitrogen/phosphorus from wastewater and NOx/sulfur from flue gas. Several novel technologies have been developed for the above pollutants removals. Furthermore, the analyses of microbial community diversity and population dynamics in natural or artificial systems are all studied by the laboratory. The flue gas desulfurization & resource recovery technology developed by the laboratory in recent years provides theoretical and technical support for the energy-saving and emission-reduction process of China.
代表性成果
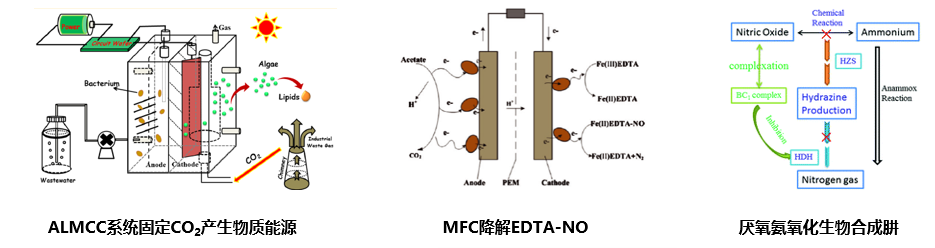
——以微生物为核心实现环境污染物的资源化/能源化处理
在提高生物降解效率的同时,探寻污染物生物降解的新机制,调控污染物降解路径实现废物资源化。
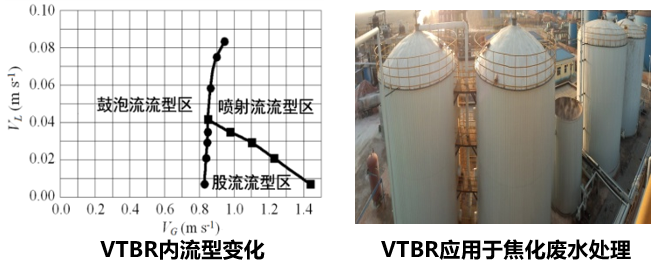
—— 垂直折流生物反应器(VTBR)的工程应用
通过气水控制系统的调控,达到不同气水耦合流态,实现高效传质。氧利用率达80%-90%,容积负荷5-11 kgCOD m-3 d-1。应用于山西潞安煤制油废水处理等27项工程。

——铁法烟气脱硫新技术的工程应用
本技术通过了教育部科技成果鉴定,被专家评价为“国内外首创、国际领先”。工程应用取得了预期的效果,脱硫效率可达96.9%,脱硫副产品聚合硫酸铁也符合国家相关产品质量标准,该技术应用于抚顺热电厂废气处理等多项工程。
代表论文
1.Tian, T., Qiao, S., Yu, C.; et al. Distinct and diverse anaerobic respiration of methanogenic community in response to MnO2 nanoparticles in anaerobic digester sludge. Water Res., 2017,123, 206-215.
2.Qiao, S.; Yin, X.; Tian, T.; et al. Hydrazine production by anammox biomass with NO reversible inhibition effect. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 4908−4915.
3.Li, J.; Jin, R.; Liu, G.; et al. Simultaneous removal of chromate and nitrate in a packed-bed bioreactor using biodegradable meal box as carbon source and biofilm carriers . Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 308−314.
4.Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Waste activated sludge fermentation liquid as carbon source for biological treatment of sulfide and nitrate in microaerobic conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 167−174.
5.Wang X., Zhang Y., Zhang T. et al.. Effect of dissolved oxygen on elemental sulfur generation in sulfide and nitrate removal process: characterization, pathway, and microbial community analysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2016, 100(6): 2895-2905.
6.Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhou, J.; et al. CO2 fixation, lipid production, and power generation by a novel air-lift-type microbial carbon capture cell system . Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10710−10717.
7.Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, M.; Dong, X.; Zhou, J. Evaluation of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification under controlled conditions by an aerobic denitrifier culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 602−605.
8.Qiao, S., Tian, T., Zhou, J.T.. Methanogenesis from wastewater stimulated by addition of elemental manganese. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 12732-12741.
9.Wang X., Zhang Y., Zhou J., et al.. Regeneration of elemental sulfur in a simultaneous sulfide and nitrate removal reactor under different dissolved oxygen conditions. Bioresour. Technol., 2015, 182: 75-81.
10.Yin, X., Qiao, S., Zhou, J.T., Quan, X.. Using three-bio-electrode reactor to enhance the activity of anammox biomass. Bioresour. Technol., 2015, 196, 376-382.